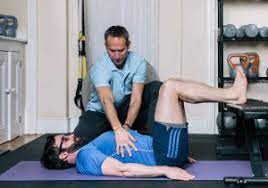
Purpose: To improve body O2 during automatic activity.
The Diaphragm is the most efficient muscle for breathing and can be used to help postural stability.
Observe how you breathe – are you an abdominal breather or a chest breather?
Chest breathing or shallow breathing lowers exercise performance because shallow breaths need more breaths to get more O2. Shallow breathing which uses mostly the neck and upper chest muscles does not fully aerate the lungs.
The Diaphragm is located horizontally between the thoracic and abdominal cavities. It is a large dome-shaped muscle at the bottom of the rib-cage (base of the lungs). Using the Diaphragm to breathe, increases exercise capacity with good oxygenation of arterial blood, it reduces shallow breaths and reduces anxiety.
Instructions:
Breathe in through the nose for 2 seconds. Purse lips – breathe out slowly for 6 seconds. Relax the shoulders and the chest. Place one hand on the chest and one hand on the stomach (stomach should move outward with inhalation, and stomach shoulder be drawn inward during exhalation). (As you breathe in, the stomach or belly should move more than the chest). Try to reconnect your brain with your diaphragm.